Nutrition and Diet
Jan 12, 2022
Asians exhibit a heightened vulnerability to type 2 diabetes, and adopting a healthy diet stands as a primary means of managing this condition. Type 2 diabetes is predominantly linked to excessive body weight, with over 85% of affected individuals classified as overweight.
Guidelines for a Healthy Diet:
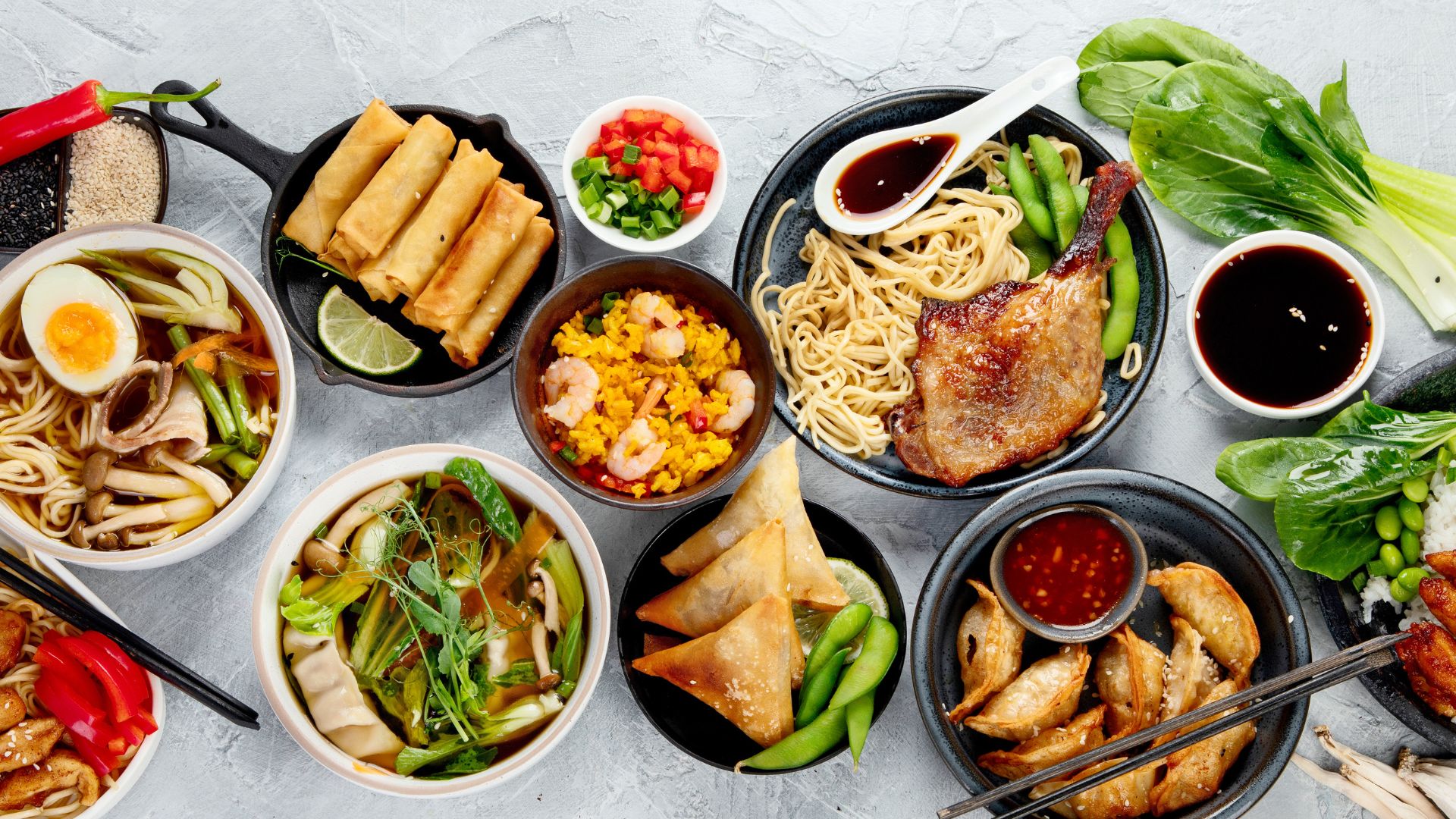
Reduce Simple, Refined Carbohydrates:
Limit consumption of simple, refined carbohydrates like white bread, white rice, and low-fiber dough-based foods.
Opt for bread and rice varieties with higher fiber content to slow absorption, minimizing the impact on blood sugar levels.
Choose 'whole grain' options for increased fiber and a lower glycemic index.
Cut Down on High-Calorie and Fried Foods:
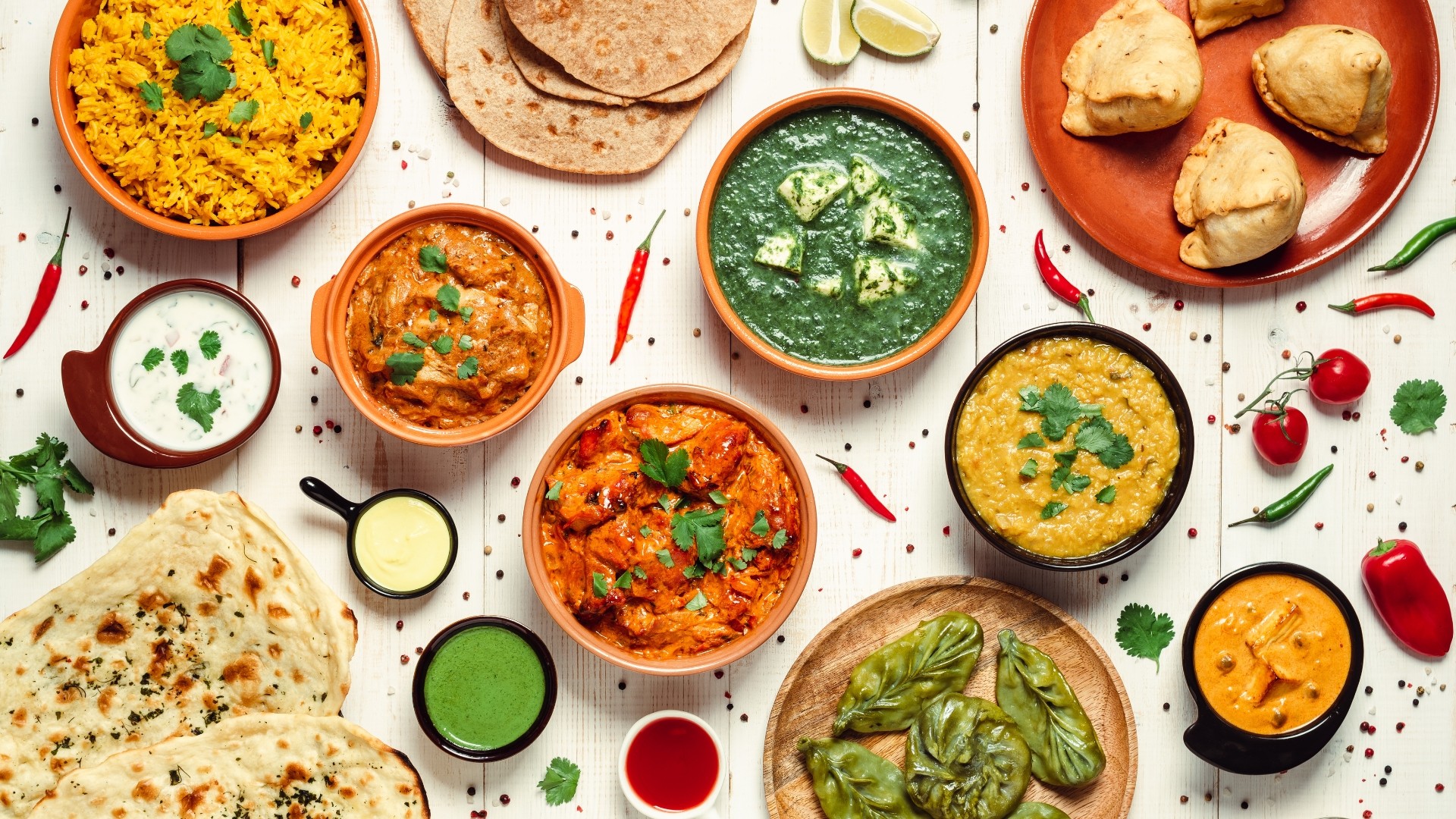
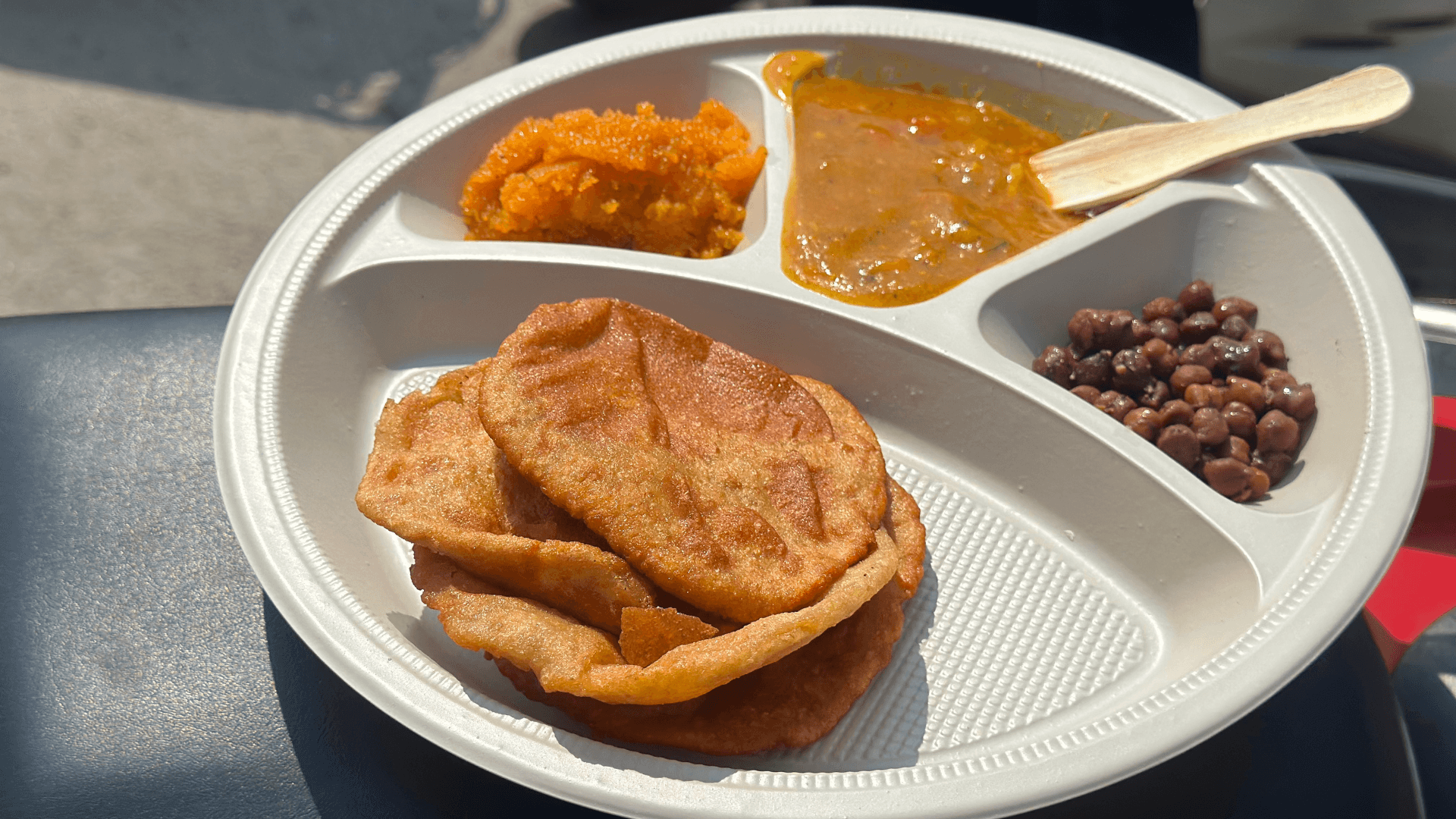
Avoid high-calorie foods that combine significant amounts of carbohydrates and saturated fat.
Be cautious with fried foods such as fried rice, samosas, onion bhajis, and masala curries.
Opt for lighter alternatives like popadoms, and consider bhuna or tandoori curries for a healthier choice.
Choose Unsaturated Fats Over Saturated Fats:
Prioritize foods rich in unsaturated fats, such as nuts, avocados, oily fish, and olive oil.
Limit intake of saturated fats found in butter, cream, yogurt, and meats.
Opt for cooking with olive oil instead of butter or ghee for reduced calories and better cholesterol management.
Have Smaller Portions:
Control portion sizes, especially with carbohydrate-rich or sugary foods, to manage blood glucose levels effectively.
Smaller portions are advisable for fatty or fried foods.
Incorporate Fresh Vegetables and Fruit:
A balanced diet should include ample fresh vegetables, with attention to their impact on blood sugar levels.
Limit portions of root vegetables like potatoes, favoring diabetes-friendly options such as cauliflower, spinach, curry leaves, cabbage, aubergine, and bell peppers.
Avoid Processed Foods:
Processed foods, often criticized for contributing to chronic health conditions like diabetes, may contain unhealthy fats and additives.
Limit the consumption of ready-made meals, scrutinize ingredient lists for additives, and opt for whole, unprocessed foods.
Monitor Salt Intake:
Keep an eye on salt levels, as excess salt is associated with high blood pressure.
Adhere to the daily recommendation of no more than 6g of salt.
Reduce salt added during cooking and avoid adding salt at the table.
Beware of processed foods, as they often contain high salt content.
Adopting these dietary guidelines can contribute significantly to managing type 2 diabetes and promoting overall health among individuals of Asian descent.